
2025 Harris Grant Report: CraftLand Project, Kurdistan Region of Iraq
Dr. Claire Padovani, CNRS Archéorient
The launch of the Crafting Landscape Project (CraftLand) in May 2025 in the Chamchamal region was made possible through the generous support of ASOR’s Charles Harris Project Grant. This pilot mission enabled the finalization and validation of a survey contract with the General Directorate of Antiquities in Erbil and the Directorate of Antiquities in Slimani, as well as the establishment of a partnership with Ashur Brick, a Kurdish company producing clay bricks in the region. In addition, we were able to test several methodological components of the project and to initiate the work in our three fields of investigation.
The objective of CraftLand is to investigate the strategies of natural resources exploitation and organisation of pottery manufacture–in relation to other economic productions–in a clay-rich environment in the Chamchamal region. This geological context, known as the Injana formation, extends over approximately 380 km² (figure 1). It is composed of sandstone, siltstone, and high quality claystone, a favourable combination for ceramic production. In Iraq, outcrops of this formation are also found near Kirkuk and the Mosul lake. The study spans from the beginnings of ceramic production to the present day, with particular emphasis on periods of major economic transformations, such as urbanisation and state formation.
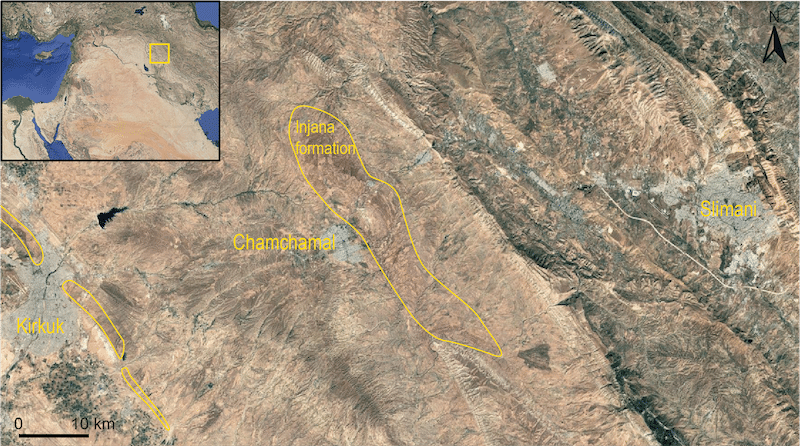
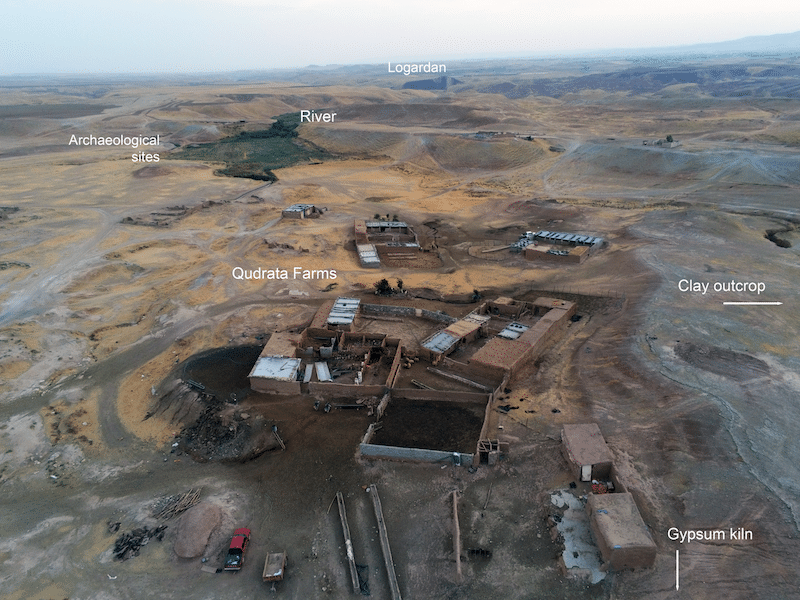
A distinctive feature of the Chamchamal’s Injana formation is its location within a zone close to cultivable lands, mineral and organic resources, formerly adjacent to woodlands, and easily connected to the Bazian Pass, a strategic route through the Qara Dagh piedmonts of the Zagros mountains. The establishment of large-scale ceramic workshops comprising dozens of kilns in the region–such as Logardan in the Early and Middle Bronze Age and Girdi Qala during the Chalcolithic and the Islamic period–suggests that the high quality of these clay resources was already recognised. Today, the Chamchamal region hosts four major brick factories supplying construction materials across Iraq, alongside traditional potters, as well as numerous farmers and pastoralists (figure 2). However, it is unlikely that raw material quality alone accounts for the recurrent and sustainable development of large-scale production in this area.
Pottery was one of the most widely used materials in ancient societies. Its production required raw materials, fuel, workforce, and access routes. CraftLand examines pottery production in its landscape and seeks to reconstruct spatial relationships between production facilities and the natural environment (raw material sources; water; topography), as well as the social and economic contexts (settlement pattern; roads; agricultural, pastoral, and other artisanal activities). Reconstructing these networks provides a valuable framework for understanding the evolution of the production organisation on a regional scale and assessing its impact on the landscape depending on the period.
To address its research questions, CraftLand employs an integrated, interdisciplinary approach organised into three complementary fields of research, with all data consolidated within a single Geographic Information System (GIS). This pilot season has already seen significant progress in the three research areas:
a) Archaeological survey
A GIS with a standardized recording protocol was implemented in collaboration with Jonathan Lisein (Gembloux Agro-Bio Tech Liege University). Thirty sites were identified through satellite imagery and have begun to be surveyed by pedestrian prospection.
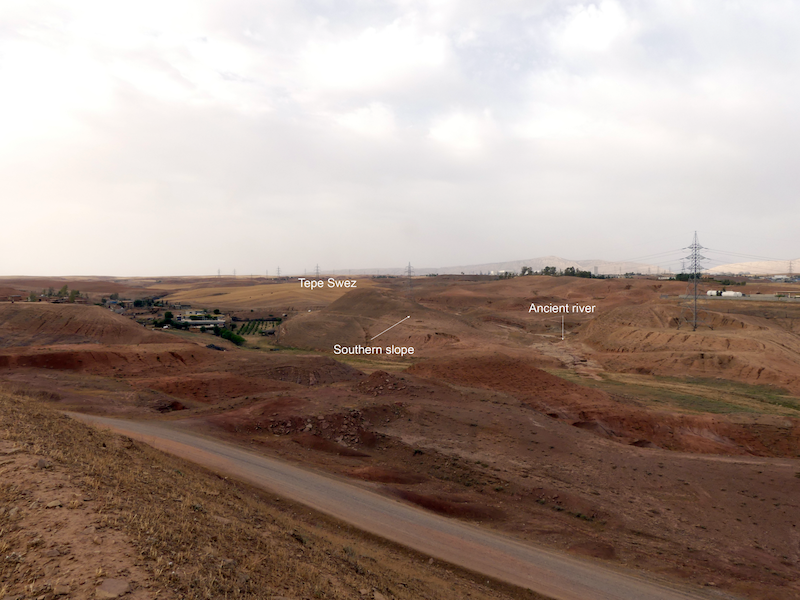
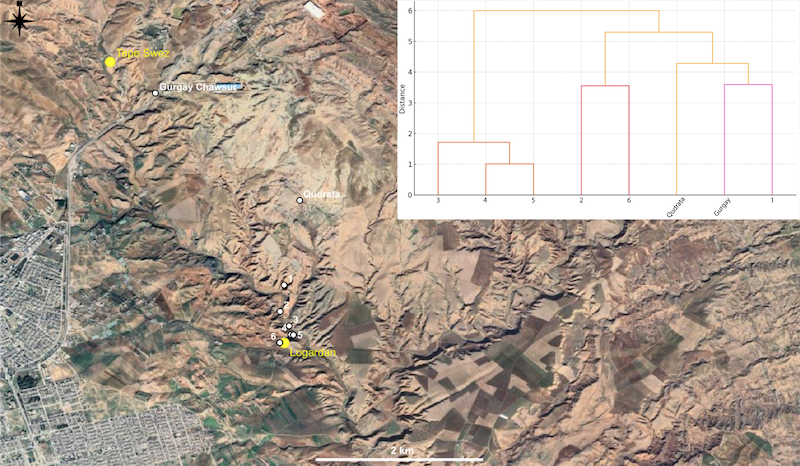
The initial priority was to test a hypothesis regarding the location of large-scale ceramic workshops in order to assess the potential for predicting their spatial distribution. Based on the conditions documented at Logardan, we hypothesized that the establishment of major pottery workshops was contingent upon specific criteria: proximity of less than 5 kilometres to a large settlement occupied at the same period, direct access to a river, and the availability of nearby clay sources. Using the GIS, Tepe Swez, a site meeting these conditions was identified and subsequently surveyed. The site is situated 3.3 kilometers from Chamchamal (ancient Azuhinum), with a river flowing at its base, and in proximity to a clay source (Gurgay Chawsur) that is used by present-day potters. On the gentler southern slope, numerous greenish fragments of large ceramic vessels were documented, together with circular alignments of burned stones organised in terraces interpreted as kiln bottoms (figure 3). Based on the pottery typology, the possible pottery production area most likely functioned during the Middle Bronze Age.

b) Landscape analyses
The project’s landscape analyses integrate geomorphology, geology, and vegetation reconstruction to identify natural raw material sources (clay, stone, and bitumen), as well as anthropogenic features (such as basins, clay pits, roads, and field terraces).
Part of this work began with the investigation of ancient clay extraction sites in the region. During the ethnographic survey (see below), we identified clay outcrops that are currently exploited by traditional potters. These extraction sites are located in close proximity to archaeological sites with important pottery production facilities (Gurgay Chawsur close to Tepe Swez and Qudrata close to Logardan). Samples were collected from these sources. A geological survey was conducted between Qudrata and Logardan in collaboration with Zirak T. Yaseen, geologist at Salahaddin University, in order to to assess whether the clay composition varies or is homogeneous within the Injana formation (figure 4).
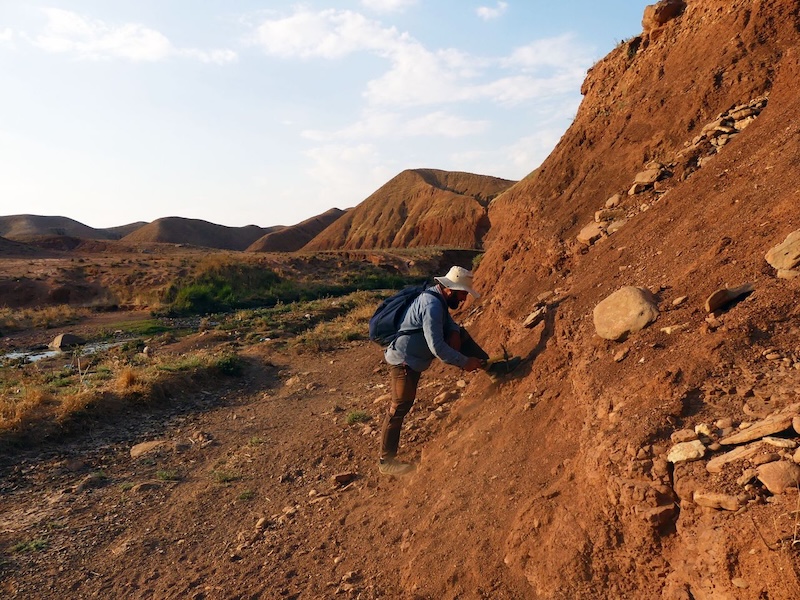

The survey documented the accessibility between sites and included sampling of multiple clay outcrops along the way. XRF analyses, conducted by Zirak T. Yaseen at the Salahaddin University in Erbil, provided preliminary results indicating that clay outcrops within the Injana Formation present various geochemical signatures. This suggests the potential to discriminate clay sources (figure 5). In collaboration with the French Archaeological Mission in the Qara Dagh directed by Johnny S. Baldi, ongoing analyses are comparing the composition of a selection of sherds from different stratigraphic levels of Logardan workshop with sampled clays. Ultimately, the possible extraction sites identified through geomorphological analyses by Luca Forti (University of Milan) will be systematically surveyed and sampled to characterize their geochemical composition. The overarching goal is to provide an open-access map of ancient clay extraction sites, including their geochemical profile, to support clay provenance studies in the region.
c) Survey of potters and clay crafts
Documentation of the actual clay production system (traditional and industrial) started with interviews using structured questionnaires and observations of practice. The survey seeks to assess the vitality of traditional pottery in relation to local industry, and to investigate sensory-based clay selection and the mechanisms of clay craft knowledge transmission.
Clay products are currently in demand (tannurs, water jars, and even living-rooms faced with unfired bricks) as people want to ‘live as in ancient times’ and maintain cultural traditions. However, local clay products remain relatively expensive–with a tannur costing around 20 dollars–and most pottery sold in local shops is imported from Iran by truck. Despite the renewed interest in ceramics, traditional potters are at risk of disappearing, as many are old and no longer pass on their craft.
The survey enabled the identification of a network of traditional clay artisans. Interviews were conducted in collaboration with Rawa Karim (Directorate of Antiquities of Slimani) and Brwa Raza (Charmo University). Preliminary results suggest that pottery and brick making may have been transmitted vertically, from one generation to the next within the same family, whereas tannur making may be more commonly transmitted horizontally, between neighbours (figure 6).
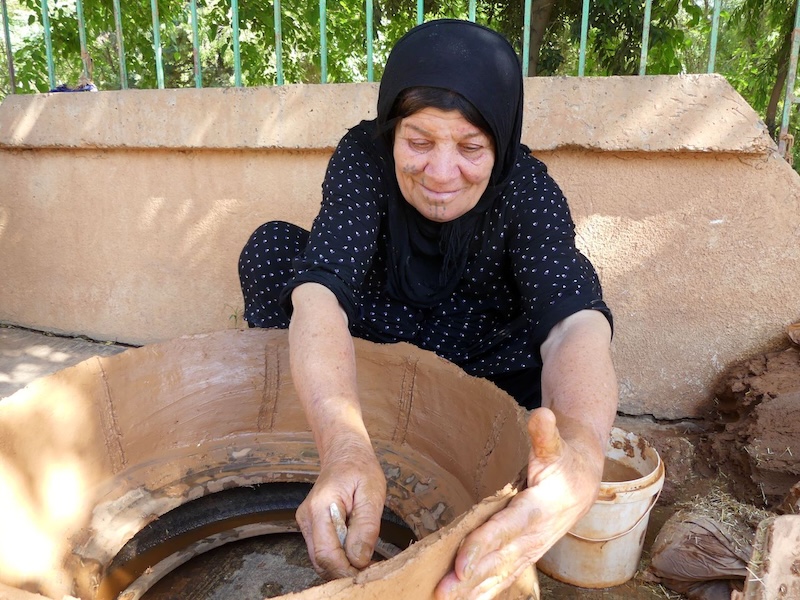

The decline of traditional pottery production is not only related to economic changes but might also be linked to the region’s recent history of political violence, notably the Anfal campaigns of the late 1980s that killed and displaced thousands of people. Although a potter’s clay source may change–often based on the reputation of the source–potters remain closely tied to their place of birth and initial apprenticeship. Beyond family ties, this connection is probably based on access to other essential ingredients for the clay matrix, such as straw used as a temper, as well as to spaces suitable for firing. Consequently, it is not uncommon for potters to return to their birthplaces to collect straw from family fields, or to stop producing pottery when these fields or firing areas are no longer accessible in their new village. This practice illustrates the deep interconnection between clay production and other economic activities, such as agriculture, as well as the critical role of spatial organisation in sustaining craft traditions. Therefore, the violent disruption of these socio-spatial networks during the Anfal probably contributed to the decline of traditional craft practices.
The results obtained in each research area are highly promising for the regional development of the project. This pilot mission strengthened ties with local communities and enterprises and initiated the survey of archaeological sites. The preliminary results also pointed to possible ways of reconstructing and interpreting production networks through spatial analysis and the recurrence of patterns, as well as through the socio-economic logics observed among present-day potter communities. The backbone of the project is to consider the social ecology of pottery production in its spatial dimension in order to understand long-term transformations in regional organisation. Subsequently, the production patterns documented in the Chamchamal region will provide points of comparison with those of other regions, helping to determine the processes and impacts of social transformations (like urbanisation and state emergence) in contrasting environments. In addition, by emphasizing the long-standing tradition of clay crafts and their influence on the landscape and the regional identity, CraftLand will leverage heritage to foster community empowerment and reinforce connections to the environment.
Latest Posts from @ASORResearch
Stay updated with the latest insights, photos, and news by following us on Instagram!
American Society of Overseas Research
The James F. Strange Center
209 Commerce Street
Alexandria, VA 22314
E-mail: info@asor.org
© 2025 ASOR
All rights reserved.
Images licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License

